Treatment options depend on the extent of the narrowing, on clinical symptoms, and on other diseases being present. For most cases, the treatment method is determined in a multidisciplinary meeting of specialists in neurosurgery, neurology and neuroradiology.
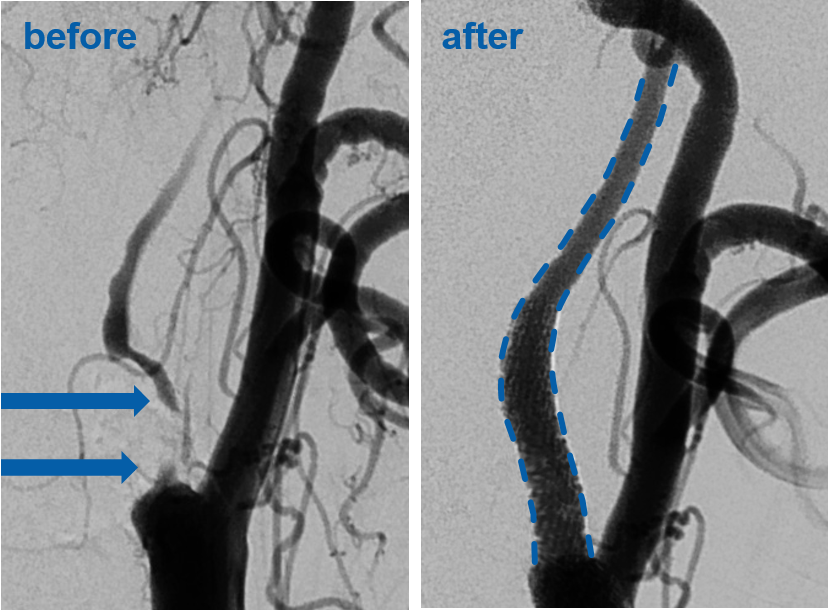
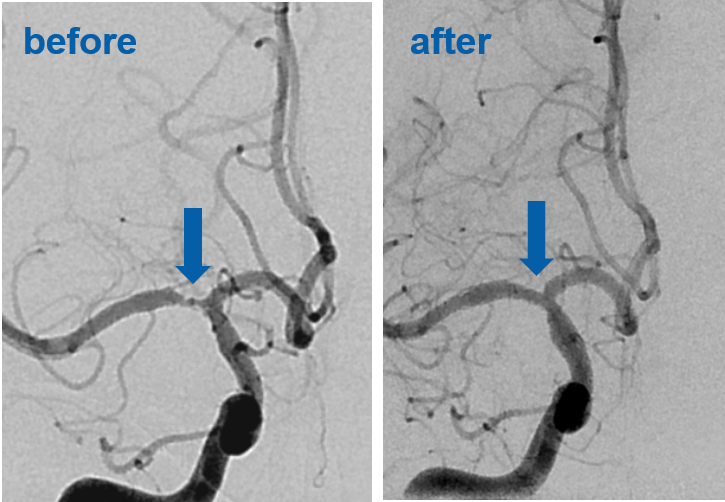
Our clinic specializes in the minimally invasive treatment of stenoses. We aim to improve the blood flow to the brain and to prevent strokes by reconstructing the carotid and cerebral arteries through the carotid artery (endovascular). Minimally invasive means that we will not directly open the blood vessel, but we will only puncture the leg artery in the groin or an artery of the upper arm or wrist. Through this opening, we then probe the diseased vessel with special catheters and materials. We first dilate the constriction with a balloon catheter (angioplasty) and then support it with a mechanical scaffold made of metal alloy (stent).